Part C
Medicare Part C, also known as a Medicare Advantage plan, is a private health insurance option that combines the coverage of Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance). Medicare Advantage plans offer all the same benefits as Original Medicare, and often include additional benefits that Original Medicare does not cover, such as hearing, dental, vision care, and wellness services.
One significant feature of Medicare Part C is that it typically has a yearly limit on out-of-pocket costs for covered medical services. This limit sets the maximum amount you can spend on healthcare expenses in a given year, offering financial protection and predictability. Original Medicare does not have a similar out-of-pocket maximum, which is one of the advantages of choosing a Medicare Advantage plan for some individuals.
To be eligible to enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan (Medicare Part C), you must meet the following criteria:
- Medicare Eligibility: You must be eligible for Medicare, which typically means you are at least 65 years old or have certain qualifying disabilities.
- Enrollment in Medicare Part A and Part B: To join a Medicare Advantage plan, you must be enrolled in both Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance).
- Reside in the Plan's Service Area: You must reside in the geographic service area covered by the specific Medicare Advantage plan you want to enroll in. Different plans are available in different regions, so you'll need to choose a plan available in your area.
- Not Have End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): In most cases, individuals with End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) cannot enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan. There are some exceptions, such as special needs plans designed for those with ESRD.
To enroll in a Medicare Advantage plan, you will typically need the following:
- Medicare Eligibility: You must be eligible for Medicare, which generally means you are at least 65 years old or have certain qualifying disabilities.
- Enrollment in Medicare Part A and Part B: To join a Medicare Advantage plan, you must be enrolled in both Medicare Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance).
- Residency in the Plan's Service Area: You must live in the geographic service area covered by the specific Medicare Advantage plan you wish to enroll in. Different plans are available in different regions, so you'll need to select a plan available in your area.
- Enrollment Period: Enroll during one of the established enrollment periods, such as the Initial Enrollment Period (when you first become eligible for Medicare), the Annual Election Period (from October 15 to December 7), or a Special Enrollment Period (for specific qualifying events).
- Identification and Personal Information: You'll need to provide personal information, including your name, address, date of birth, and Medicare number.
- Additional Information: Some Medicare Advantage plans may request additional information, such as details about your existing healthcare coverage, prescription medications, and any special needs or preferences.
When you join a Medicare Advantage Plan, you will have to give these:
- Your Medicare number
- The date your Part A and/or Part B coverage started (can be found in your Medicare card)
The right Medicare Advantage plan for you depends on your individual healthcare needs, budget, and preferences. To choose the best plan, assess your healthcare requirements, compare available options, check provider networks, and consider your budget. Consulting an advisor can also be helpful in making an informed decision.
Most Common Types of Medicare Advantage Plans
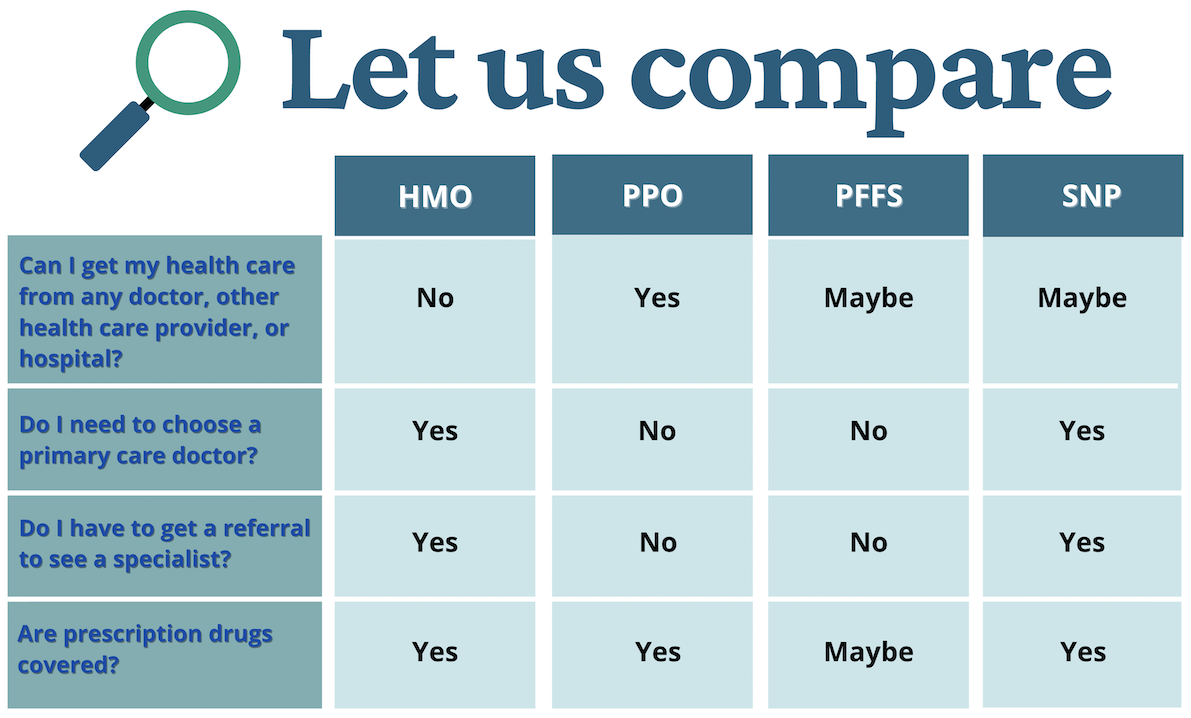
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) Plans
The plan may require members to get referrals from a primary care physician in order to see specialists in their network. They may also change coverage and/or premiums annually. There may be additional costs such as hospital and skilled nursing facility co-payments.
There may be prior authorization (approval) requirements for certain services. Also, providers can choose to no longer participate with an HMO plan during the year. Even participating providers may decide at any point that they are not accepting new patients under the Medicare HMO plan. Generally, members are required to use only healthcare providers in the HMO plan’s network.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
PPOs provide some coverage for services provided outside of their network. Cost-sharing amounts will usually be lower when beneficiaries use network providers than when they use out-of-network providers. A PPO must have a sufficient network of providers so that enrollees can get all services within the plan. Also, with a PPO, a member does not have to get a referral to see a specialist. Premiums are usually more than HMO premiums, but less than premiums for Medicare Supplement insurance.
Private Fee-for-Service (PFFS) Plans
This type of plan sets its own payment structure. The plan decides how much it will pay its Medicare providers, and how much you will pay as a patient. Under this plan, a person with Medicare may go to any Medicare-participating medical provider or any hospital, as long as the provider or hospital accepts the plan’s payment terms. PFFS plans also have networks of providers and are very similar to PPO plans. No referrals are necessary. Costs may include a monthly premium and an amount per visit or service.
Special Needs Plans (SNP)
This plan is designed to serve people with specific health conditions, or meet certain other qualifications. It is only available for those with both Medicare and Medicaid (which may include those with QMB only without Medicaid), institutionalized beneficiaries or those with certain chronic conditions. SNPs may offer more focused and specialized health care as well as better coordination of care for these beneficiaries than other types of Medicare Advantage plans. All SNPs include Part D drug coverage.